Metabolic reprogramming is a hallmark of cancer and plays an important role in driving cell proliferation, with amino acid metabolic rewiring being particularly prevalent in malignancies. One example is arginine which, besides being required for protein synthesis and as a precursor for polyamines, creatine, and nitric oxide, is also a metabolic regulator. While disruption of key enzymes involved in arginine metabolism (e.g., ASS1) has been noted in human cancers, there is little data on arginine levels in tumor cells.
In their new study, Mossmann et al. describe how altered arginine metabolism contributes to the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (1). The team first used an mTOR-driven HCC mouse model (L-dKO) to show enrichment of arginine in HCC tumors due to increased arginine uptake. Importantly, the elevated arginine level is essential for tumorigenicity, and two enzymes responsible for arginine-to-polyamine conversion are downregulated in an early step of tumorigenesis. The authors then identified a human liver cancer cell line (i.e., SNU-449) that phenocopies the metabolic findings in the L-dKO mice in order to further elucidate arginine’s role in oncogenesis. Implementing a series of elegant experiments, they determined that unmetabolized arginine transcriptionally alters the metabolism of liver cancer cells in ways that include enhanced production of asparagine, a facilitator of arginine uptake. Arginine elicits this metabolic reprogramming (and positive feedback loop) through binding to the RNA-binding protein RBM39, which is both a pre-mRNA splicing factor and a transcriptional regulator. The researchers then revealed that the aryl sulfonamide indisulam, which triggers proteasomal degradation of RBM39, reverses the gene expression signature characteristic of the tumors and decreased tumor progression in the L-dKO mice. Most excitingly, analysis of human HCC patient samples and HCC-derived organoids recapitulated the L-dKO mouse and human cell studies, which will undoubtedly lead to further research with potentially significant clinical ramifications for HCC therapy.
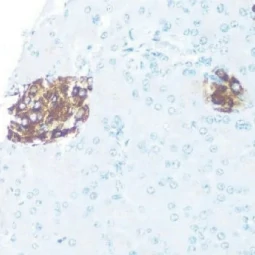
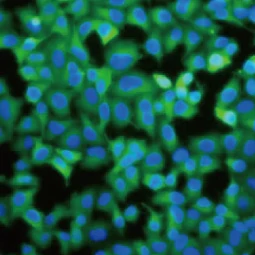
GeneTex offers an extensive catalog of quality antibodies and reagents for cancer metabolism, including the Arginase 1 antibody (GTX109242), ODC antibody (GTX54600), Asparagine synthetase antibody (GTX30068), PSAT1 antibody [GT1353] (GTX633629), and PSPH antibody (GTX33442) cited in the Mossmann et al. study. In addition, GeneTex wants to introduce its extensively validated recombinant rabbit monoclonal Arginase 1 antibody [HL1891] (GTX637640) and PSAT1 antibody [HL2270] (GTX638322). For more information, please see the product images below and visit www.genetex.com.
Highlighted Products
Reference:
- Cell. 2023 Nov 9;186(23):5068-5083.e23. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.09.011.
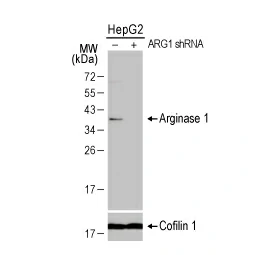
![Arginase 1 antibody [HL1891] (GTX637640) Arginase 1 antibody [HL1891] (GTX637640)](/upload/media/MarketingMaterial/Newsletter/2024/W06_ArticleAlert/landingPage_img_255x255_02.webp)
![PSAT1 antibody [GT1353] (GTX633629) PSAT1 antibody [GT1353] (GTX633629)](/upload/media/MarketingMaterial/Newsletter/2024/W06_ArticleAlert/landingPage_img_255x255_05.webp)
![PSAT1 antibody [HL2270] (GTX638322) PSAT1 antibody [HL2270] (GTX638322)](/upload/media/MarketingMaterial/Newsletter/2024/W06_ArticleAlert/landingPage_img_255x255_06.webp)
![mTOR antibody [HL2216] (GTX638220) mTOR antibody [HL2216] (GTX638220)](/upload/media/MarketingMaterial/Newsletter/2024/W06_ArticleAlert/landingPage_img_255x255_08.webp)
![LAT1 / SLC7A5 antibody [HL2353] (GTX638556) LAT1 / SLC7A5 antibody [HL2353] (GTX638556)](/upload/media/MarketingMaterial/Newsletter/2024/W06_ArticleAlert/landingPage_img_255x255_09.webp)