Exosomes, extracellular vesicles released by most cell types, facilitate cell-to-cell communication through transfer of biomolecules (including lipids, proteins, mRNA, and non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs)) to recipient cells. Increasing evidence links exosomes to cancer metastasis, with many examples of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) in the exosomal cargo contributing to metastasis of various human malignancies. In the case of lung cancer, one of the most common and most lethal cancers worldwide, there is a great need to learn more about how exosomal lncRNAs drive metastasis.
A new study by Hsu et al. makes a major contribution to our understanding of exosomal lncRNA-mediated metastasis of lung cancer (LC) through the discovery of a novel lncRNA and its apparent mechanism of action (1). The team began their inquiry by observing that conditioned media (CM) from highly metastatic LC cells induces enhanced migratory and invasive behavior of LC cells with poor metastatic ability, and that this was dependent on exosomes in the CM. Through exosomal lncRNA-seq they identified a specific lncRNA, named lnc-MLETA1 (metastatic lung cancer cell-derived exosome transmitted lncRNA 1), which was “significantly upregulated” in highly metastatic LC cells. The researchers then demonstrated that exosome-transmitted lnc-MLETA1 increases both the migratory and invasive capabilities of the LC cells with low metastatic potential, and also promoted lung cancer metastasis in mouse models. Mechanistically, lnc-MLETA1 was shown to act as a sponge of the microRNAs miR-186-5p and miR-497-5p, which were shown to regulate EGFR and IGF1R expression, respectively. Finally, exosomal lnc-MLETA1 detection in plasma from LC patients was found to correlate with metastasis. The findings by Hsu et al. shed light on the novel role of exosomal lnc-MLETA1 in mediating communication between lung cancer cells, ultimately promoting metastasis. In addition, lnc-MLETA1 may have utility as a biomarker or even a therapeutic target.
GeneTex offers an extensive catalog of quality antibodies and reagents for exosome research, including the TSG101 antibody (GTX118736), Flotillin 1 antibody [C3], C-term (GTX104769), and Calnexin antibody [C3], C-term (GTX109669) cited in the Hsu et al. study. In addition, GeneTex is excited to introduce its extensively validated recombinant rabbit monoclonal TSG101 antibody [4A10-RB] (GTX635396) and Calnexin antibody [HL1598] (GTX637077). For more information, please see the product data images below and visit www.genetex.com.
Highlighted Products
Reference:
- J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023 Oct 26;42(1):283. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02859-y.
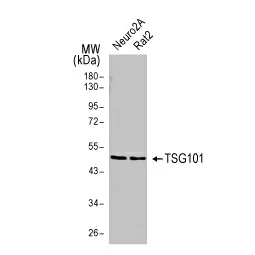
![TSG101 antibody [4A10-RB] (GTX635396) TSG101 antibody [4A10-RB] (GTX635396)](/upload/media/MarketingMaterial/Newsletter/2024/W04_ArticleAlert/landingPage_img_255x255_02.webp)
![Flotillin 1 antibody [C3], C-term (GTX104769) Flotillin 1 antibody [C3], C-term (GTX104769)](/upload/media/MarketingMaterial/Newsletter/2024/W04_ArticleAlert/landingPage_img_255x255_03.webp)
![Calnexin antibody [C3], C-term (GTX109669) Calnexin antibody [C3], C-term (GTX109669)](/upload/media/MarketingMaterial/Newsletter/2024/W04_ArticleAlert/landingPage_img_255x255_04.webp)
![Calnexin antibody [HL1598] (GTX637077) Calnexin antibody [HL1598] (GTX637077)](/upload/media/MarketingMaterial/Newsletter/2024/W04_ArticleAlert/landingPage_img_255x255_05.webp)
![Annexin A1 antibody [HL2141] (GTX638119) Annexin A1 antibody [HL2141] (GTX638119)](/upload/media/MarketingMaterial/Newsletter/2024/W04_ArticleAlert/landingPage_img_255x255_06.webp)
![Hsp70 antibody [HL1580] (GTX637059) Hsp70 antibody [HL1580] (GTX637059)](/upload/media/MarketingMaterial/Newsletter/2024/W04_ArticleAlert/landingPage_img_255x255_07.webp)
![RAB5A antibody [HL1497] (GTX636971) RAB5A antibody [HL1497] (GTX636971)](/upload/media/MarketingMaterial/Newsletter/2024/W04_ArticleAlert/landingPage_img_255x255_08.webp)
![CD81 antibody [HL1666] (GTX637264) CD81 antibody [HL1666] (GTX637264)](/upload/media/MarketingMaterial/Newsletter/2024/W04_ArticleAlert/landingPage_img_255x255_09.webp)